argon core electrons|Iba pa : Baguio The electron configurations of silicon (14 electrons), phosphorus (15 electrons), sulfur (16 electrons), chlorine (17 electrons), and argon (18 electrons) are analogous in the .
UST Angelicum College Student Portal. Sign in to start your session. Password format: lastnamemmddyyyy. Ex. tomas07051972. Sign In. For log-in concerns call 87121745 or 7324243 loc. 106.
argon core electrons,The electrons of an atom are typically divided into two categories: valence and core electrons. Valence electrons occupy the outermost shell or highest energy level of an atom while core electrons are those occupying the innermost shell or lowest energy levels. Tingnan ang higit paIn this module, the conceptions of valence and core electrons are put forward and explained in the introduction. The general rule of relationship between . Tingnan ang higit paThe chemical reactivity of an atom is mainly determined by valence electrons. Atoms which have a complete shell of valence electrons tend to be . Tingnan ang higit pa
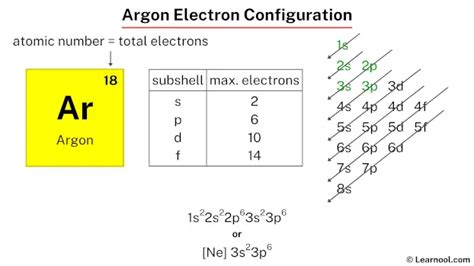
argon core electronsThe chemical reactivity of an atom is mainly determined by valence electrons. Atoms which have a complete shell of valence electrons tend to be . Tingnan ang higit paIba paMiessler, Gary L., and Donald A. Tarr. Inorganic Chemistry. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2010. Print. Brown, Ian David. The . Tingnan ang higit pa The arrangement of electrons in argon in specific rules in different orbits and orbitals is called the electron configuration of argon. The electron configuration of argon is [ Ne] 3s 2 3p 6 , if the electron .The electron configurations of silicon (14 electrons), phosphorus (15 electrons), sulfur (16 electrons), chlorine (17 electrons), and argon (18 electrons) are analogous in the .
In order to write the Argon electron configuration we first need to know the number of electrons for the Ar atom (there are 18 electrons). When we write the configuration we'll .Element Argon (Ar), Group 18, Atomic Number 18, p-block, Mass 39.95. Sources, facts, uses, scarcity (SRI), podcasts, alchemical symbols, videos and images. Jump to main .We will call these core electrons. For the representative elements (columns 1, 2, and 13-18 of the Periodic Table), the core electrons are all electrons with an n-value lower than . We can see from the electron configuration of a carbon atom—1 s2 2 s2 2 p2 —that it has 4 valence electrons (2 s2 2 p2) and 2 core electrons (1 s2 ). You will see in .
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell, or energy level, of an atom. For example, oxygen has six valence electrons, two in the 2s subshell and four in the 2p subshell. We can write the configuration of oxygen's valence electrons as . Periodic trends (such as electronegativity, electron affinity, atomic and ionic radii, and ionization energy) can be understood in terms of Coulomb's law, which is Fₑ = (q₁q₂)/r².Core electrons are the electrons in an atom that are not valence electrons and do not participate in chemical bonding. The nucleus and the core electrons of an atom form the .
Valence shell electrons (or, more simply, the valence electrons) are the electrons in the highest-numbered shell, or valence shell, while core electrons are the electrons in lower-numbered shells. We can see from the electron configuration of a carbon atom—1 s2 2 s2 2 p2 —that it has 4 valence electrons (2 s2 2 p2) and 2 core . Bohr diagrams indicate how many electrons fill each principal shell. Group 18 elements (helium, neon, and argon are shown in Figure 2) have a full outer, or valence, shell. A full valence shell is the most stable electron configuration. Elements in other groups have partially filled valence shells and gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable .For example, in the sodium atom the highest n-value is 3. Thus, the core electrons are those in the atomic orbitals with n < 3, namely those in the 1s, 2s and 2p orbitals. . orbitals are filled, one electron at a time. This row concludes with the noble gas argon, which has the electron configuration [Ne] 3s 2 3p 6, corresponding to a filled .
Argon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. [9] Argon is the third most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv ). It is more than twice as abundant as water vapor (which averages about 4000 ppmv, but varies greatly), 23 times as abundant as . The core electrons are 10. 2. The valence electrons are 8. Core electrons are electrons located in the inner shells of and atom. Valence electrons are electrons located on the outermost shell of an atom. From the question given above, we obtained: Ar (18) => [Ne] 3s²3p⁶. Recall. Ne (10) => 1s² 2s²2p⁶. Therefore, Ar (18) => [1s² .

Valence electrons: For main group elements (i.e s-block and p-block elements), the valence electrons are the electrons present in the outermost orbit. . the valence electrons are the electrons present in the shells outside the noble gas core. If you want a Periodic table with Valence electrons, . Argon (Ar) 8: 19: Potassium (K) 1: 20 . They are helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. A noble gas configuration of an atom consists of the elemental symbol of the last noble gas prior to that atom, followed by the configuration of the remaining electrons. So for sodium, we make the substitution of [Ne] [ Ne] for the 1s22s22p6 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 part of the configuration.Argon provides an inert atmosphere in which welded metals will not oxidise. Appearance. Argon is a colourless, odourless gas that is totally inert to other substances. Uses. Argon is often used when an inert atmosphere is needed. It is used in this way for the production of titanium and other reactive elements.Contributors and Attributions. 3.10: Valence Electrons is shared under a CC BY-NC license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied principal energy level of an atom. In the second period elements, the two electrons in the 1s sublevel are called inner-shell electrons .. Inner transition elements are metallic elements in which the last electron added occupies an f orbital. They are shown in green in Figure 3.4.6 3.4. 6. The valence shells of the inner transition elements consist of the ( n – 2) f, the ( n – 1) d, and the ns subshells. There are two inner transition series:

Electron configuration chart of all Elements is mentioned in the table below.The Shorthand electron configuration (or Noble gas configuration) as well as Full . Electron configuration of Argon (Ar) .
argon core electrons Iba pa Potassium has the same electron configuration as an argon +1 electron. We can make this point when we write electronic configuration codes. : : Therefore, : [] (This is . All electrons other than valence electrons are called core electrons. These electrons are in inner energy levels. It would take a very large amount of energy to pull an . Since the core electron shells correspond to noble gas electron configurations, we can abbreviate electron configurations by writing the noble gas that matches the core electron configuration, . Argon for example has a completely full first shell, second shell, and third shell, and then to build calcium, will then have two electrons in that fourth shell, so it is argon and then 4s2. So .Assigning Electron Configuration . We write electronic configurations by following the aufbau principle (from German, meaning “building up”). First we determine the number of electrons in the atom; then we add electrons one at a time to the lowest-energy orbital available without violating the Pauli Exclusion Principle .That is, recognizing that each .
They are helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. A noble gas configuration of an atom consists of the elemental symbol of the last noble gas prior to that atom, followed by the configuration of the remaining electrons. So for sodium, we make the substitution of [Ne] [ Ne] for the 1s22s22p6 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 part of the configuration.
Valence shell electrons (or, more simply, the valence electrons) are the electrons in the highest-numbered shell, or valence shell, while core electrons are the electrons in lower-numbered shells. We can see from the electron configuration of a carbon atom—1 s2 2 s2 2 p2 —that it has 4 valence electrons (2 s2 2 p2) and 2 core .
Argon contains 18 electrons, so calcium contains 18 core electrons. Note that the valence electrons are often all of those after the noble gas core, but not always. Valence = The 5p sublevel is unfilled, so the 5p and 5s .
argon core electrons|Iba pa
PH0 · which ion is isoelectronic with ar
PH1 · number of electrons in argon
PH2 · how to find core electrons
PH3 · electron shell rules
PH4 · electron configuration of argon
PH5 · electron arrangement of argon
PH6 · core electrons in ne
PH7 · argon orbitals
PH8 · Iba pa